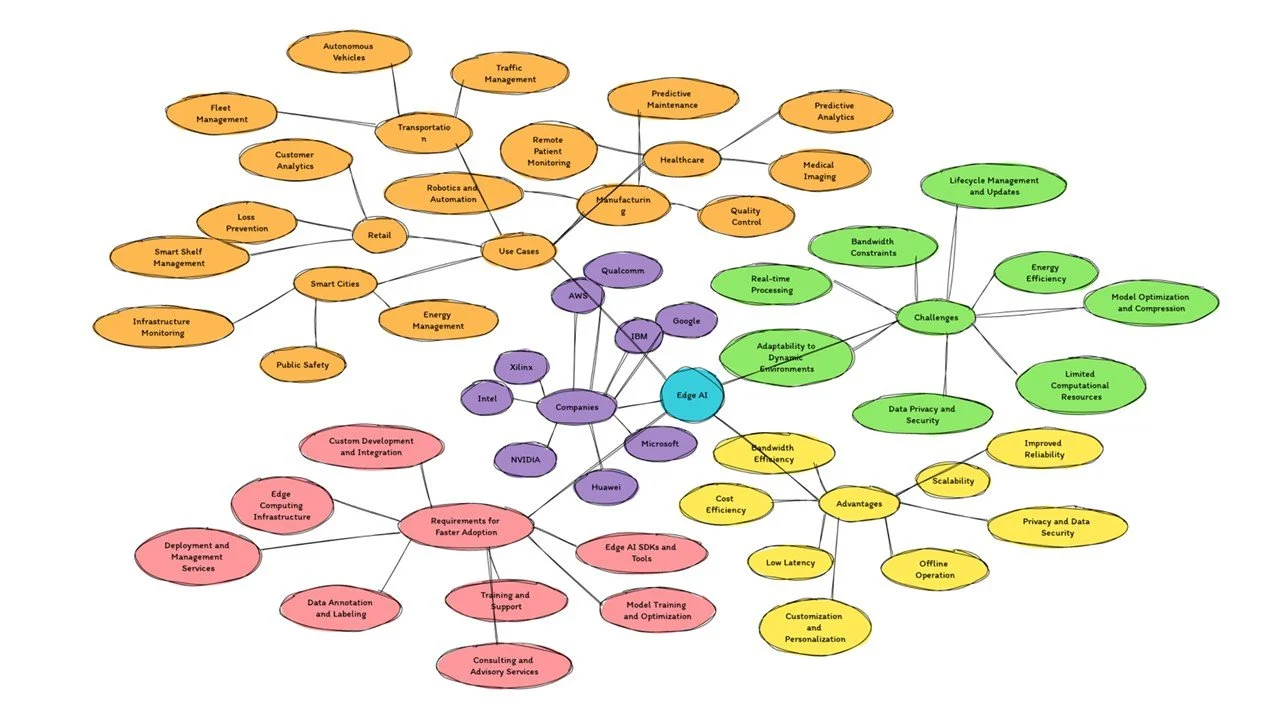
Edge AI: Advantages, Challenges and Use Cases
Introduction
In the ever-evolving realm of artificial intelligence (AI), the emergence of edge AI stands as a transformative breakthrough. Unlike traditional AI approaches reliant on centralized cloud servers, edge AI brings computational intelligence directly to the devices where data is generated, processed, and acted upon. This paradigm shift offers a myriad of compelling advantages over its cloud-based counterparts. By harnessing the power of local processing, edge AI significantly reduces latency, enabling real-time decision-making critical for applications ranging from autonomous vehicles to industrial automation and augmented reality. Moreover, edge AI enhances privacy and data security by keeping sensitive information on-device, mitigating risks associated with transmitting data to external servers. Its capability for offline operation ensures seamless functionality even in environments with limited or no internet connectivity, fostering continuous operation in remote or isolated settings.
Additionally, edge AI optimizes bandwidth usage, alleviating strain on network infrastructure, particularly in scenarios where bandwidth is limited or expensive. Furthermore, its local processing capability enhances reliability, scalability, customization, and cost efficiency, making it a versatile and powerful approach for deploying AI applications across diverse industries. Illustration of the overall concept is provided in Fig 1.
Fig 1: Edge AI concept
Advantages of Edge AI
Edge AI offers several advantages over traditional cloud-based AI approaches:
Low Latency: By performing AI computations locally on edge devices, latency is significantly reduced since data doesn't need to be transmitted to remote servers for processing. This enables real-time decision-making, critical for applications such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and augmented reality.
Privacy and Data Security: Edge AI allows sensitive data to remain on the device, reducing the risk of data breaches or privacy violations associated with transmitting data to the cloud. This is particularly important for applications involving personal health information, surveillance, or sensitive industrial data.
Offline Operation: Edge AI enables devices to operate even when disconnected from the internet or in environments with limited connectivity. This ensures continuous functionality and allows applications to remain operational in remote or isolated locations where internet access is unavailable or unreliable.
Bandwidth Efficiency: Edge AI reduces the need for frequent data transfers over the network, leading to lower bandwidth usage and reduced strain on network infrastructure. This is advantageous in scenarios where network bandwidth is limited or expensive, such as in remote areas or in deployments involving many devices.
Improved Reliability: By processing data locally, edge AI systems are less susceptible to disruptions caused by network outages or latency spikes. This enhances the reliability and robustness of applications, particularly those operating in dynamic or unpredictable environments.
Scalability: Edge AI facilitates distributed computing by distributing AI processing across multiple edge devices. This allows for scalable deployments without overloading centralized servers or requiring significant infrastructure upgrades.
Customization and Personalization: Edge AI enables customization and personalization of AI models to suit specific user preferences or requirements. Models can be tailored and optimized for individual devices or user profiles, leading to more personalized experiences and improved performance.
Cost Efficiency: Edge AI reduces the need for continuous data transmission and storage in the cloud, resulting in lower operational costs associated with network bandwidth, cloud computing resources, and data storage. This makes edge AI more cost-effective, especially for applications deployed at scale.
Overall, Edge AI offers a versatile and powerful approach to deploying artificial intelligence applications, particularly in scenarios where low latency, privacy, offline operation, and scalability are paramount.
Challenges of edge AI
Edge AI, which involves performing artificial intelligence computations on local devices rather than relying on centralized servers or cloud computing, faces several technical challenges:
Limited Computational Resources: Edge devices often have limited processing power, memory, and energy compared to cloud servers. This constraint necessitates efficient algorithms and models tailored for edge deployment, as traditional deep learning models might be too computationally intensive.
Energy Efficiency: Edge devices are often battery-powered or have limited access to power sources. Thus, energy efficiency is crucial to prolong the device's battery life and ensure continuous operation. AI algorithms must be optimized for low power consumption without compromising performance.
Bandwidth Constraints: Edge devices may have limited or intermittent connectivity to the internet, making it impractical to rely on cloud servers for AI processing. Performing AI computations locally reduces the need for frequent data transfers over the network, minimizing bandwidth usage and latency.
Data Privacy and Security: Edge AI systems often process sensitive data locally, such as personal health information or surveillance footage. Ensuring data privacy and security becomes challenging, as the data may be vulnerable to theft or tampering if adequate safeguards are not in place.
Real-time Processing: Certain applications, such as autonomous vehicles or industrial automation, require real-time AI processing to make split-second decisions. Achieving low-latency inference on edge devices is critical for these applications to ensure timely responses to changing environments.
Adaptability to Dynamic Environments: Edge devices operate in diverse and dynamic environments, where conditions can change rapidly. AI models deployed on the edge must be robust and adaptable to variations in data distribution, lighting conditions, or device characteristics.
Model Optimization and Compression: To fit AI models onto edge devices with limited storage capacity and computational resources, techniques such as model compression, quantization, and pruning are essential. These methods reduce the size of the model and the number of computations required for inference while preserving accuracy.
Lifecycle Management and Updates: Managing a large number of edge devices distributed across different locations poses challenges in deploying, updating, and maintaining AI models. Efficient mechanisms for model deployment, version control, and over-the-air updates are necessary to ensure the reliability and performance of edge AI systems.
Addressing these challenges requires interdisciplinary research and innovation in areas such as machine learning, computer vision, signal processing, embedded systems, and cybersecurity. Additionally, advancements in hardware technologies, such as low-power processors and specialized accelerators, play a crucial role in enabling edge AI applications.
Companies working on Edge AI solutions
Several companies are actively working on developing edge AI solutions across various industries. Here are some notable examples:
NVIDIA: NVIDIA offers a range of edge AI solutions, including the NVIDIA Jetson series of embedded AI computing platforms. These platforms provide high-performance AI capabilities for applications such as robotics, autonomous vehicles, and smart cameras.
Intel: Intel provides edge AI solutions through its lineup of processors, accelerators, and software frameworks optimized for AI inference at the edge. Intel's OpenVINO toolkit enables developers to deploy AI models efficiently on Intel hardware platforms.
Google: Google has been investing in edge AI solutions through products like Coral, which includes hardware accelerators and software tools for running machine learning models on edge devices. Google also offers TensorFlow Lite, a lightweight framework for deploying machine learning models on mobile and embedded devices.
Microsoft: Microsoft offers Azure IoT Edge, a platform for deploying cloud services, including AI and machine learning, to edge devices. Azure IoT Edge enables developers to run AI workloads locally on devices, improving latency and reducing reliance on cloud connectivity.
Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS provides edge AI solutions through services like AWS IoT Greengrass, which extends AWS cloud capabilities to edge devices. AWS IoT Greengrass enables local execution of machine learning inference and other AI workloads on connected devices.
Qualcomm: Qualcomm offers a range of processors and platforms optimized for edge AI applications, particularly in the mobile and IoT sectors. Qualcomm's Snapdragon series of processors integrate AI accelerators to enable efficient on-device AI processing.
IBM: IBM offers edge AI solutions through its Watson IoT platform, which includes tools for deploying AI and analytics capabilities to edge devices. IBM Edge Application Manager enables organizations to manage and deploy AI workloads across distributed edge environments.
Huawei: Huawei provides edge AI solutions through its Ascend series of AI processors and AI computing platforms. Huawei's AI solutions are used in various applications, including smart cities, intelligent transportation, and industrial automation.
Xilinx: Xilinx offers edge AI solutions through its adaptive computing platforms, including FPGAs and adaptive SoCs. Xilinx's platforms enable efficient acceleration of AI workloads at the edge, providing flexibility and performance for diverse applications.
These companies, along with many others, are driving innovation in edge AI technology and enabling a wide range of applications across industries such as healthcare, automotive, manufacturing, and smart cities.
Use cases of Edge AI solutions
Edge AI solutions have numerous applications across various industries, enabling real-time processing, improved efficiency, and enhanced decision-making capabilities. Here are some examples of how edge AI is being used in different sectors:
Healthcare:
a. Remote Patient Monitoring: Edge AI enables wearable devices to monitor vital signs and detect abnormalities in real-time, allowing healthcare providers to remotely monitor patients' health conditions and intervene as necessary.
b. Medical Imaging: Edge AI can be used for on-device processing of medical images, such as X-rays and MRI scans, to assist radiologists in diagnosing conditions more quickly and accurately.
c. Predictive Analytics: Edge AI algorithms deployed on medical devices can analyze patient data to predict health outcomes, identify early warning signs of diseases, and personalize treatment plans.
2. Retail:
a. Smart Shelf Management: Edge AI cameras installed on retail shelves can analyze product inventory in real-time, detecting stock levels, identifying misplaced items, and providing insights to optimize shelf layout and product placement.
b. Customer Analytics: Edge AI systems can analyze customer behavior and preferences in-store, enabling retailers to offer personalized recommendations, improve marketing strategies, and enhance the overall shopping experience.
c. Loss Prevention: Edge AI-powered surveillance cameras can detect suspicious behavior, such as shoplifting or vandalism, in real-time, allowing store staff to intervene immediately and prevent losses.
3. Manufacturing:
a. Predictive Maintenance: Edge AI sensors installed on manufacturing equipment can monitor machine health and detect anomalies indicative of potential failures, enabling proactive maintenance to minimize downtime and reduce maintenance costs.
b. Quality Control: Edge AI systems can analyze images of manufactured products to identify defects or deviations from quality standards, ensuring product quality and reducing waste.
c.Robotics and Automation: Edge AI enables robots and autonomous systems to perform tasks such as object recognition, navigation, and manipulation in real-time, enhancing efficiency and flexibility in manufacturing processes.
4. Transportation:
a. Autonomous Vehicles: Edge AI is essential for autonomous vehicles to perceive their surroundings, detect obstacles, and make real-time driving decisions without relying on continuous connectivity to the cloud.
b. Traffic Management: Edge AI systems deployed on roadside infrastructure can analyze traffic flow, detect congestion, and optimize traffic signals in real-time to improve traffic efficiency and reduce congestion.
c.Fleet Management: Edge AI sensors installed on vehicles can monitor driver behavior, vehicle performance, and cargo conditions, enabling better fleet management, route optimization, and predictive maintenance.
5. Smart Cities:
a. Public Safety: Edge AI-powered surveillance cameras can analyze video feeds to detect and respond to security threats, monitor crowds, and assist law enforcement in crime prevention and investigation.
b. Infrastructure Monitoring: Edge AI sensors deployed on bridges, roads, and other infrastructure can monitor structural health, detect defects, and assess risks to ensure timely maintenance and prevent accidents.
c.Energy Management: Edge AI systems can optimize energy usage in buildings, streetlights, and other infrastructure by analyzing data from sensors and adjusting energy consumption based on demand and environmental conditions.
These examples demonstrate the versatility and potential impact of edge AI across a wide range of industries, driving innovation, efficiency, and improved decision-making capabilities.
Companies that have a solution for Edge AI use cases
Several companies offer solutions for edge AI across various industries. Here are examples of companies and their edge AI solutions tailored for different use cases:
1. Healthcare:
a. Philips: Offers edge AI solutions for healthcare applications such as patient monitoring, medical imaging, and predictive analytics. Their IntelliVue Guardian solution enables real-time patient monitoring and predictive analytics for early deterioration detection.
b. Biofourmis: Provides edge AI-powered wearable devices for remote patient monitoring and personalized healthcare management. Their Biovitals platform analyzes physiological data in real-time to predict health deterioration and provide personalized interventions.
2. Retail:
a. Trax: Offers computer vision-based edge AI solutions for retail shelf monitoring and inventory management. Their Retail Watch solution uses edge devices equipped with cameras to analyze shelf conditions, detect out-of-stock items, and optimize shelf layout.
b. Hikvision: Provides edge AI-powered surveillance cameras and video analytics solutions for retail security and customer analytics. Their DeepinView series cameras utilize on-device AI processing to detect suspicious behavior, monitor foot traffic, and analyze customer demographics.
3. Manufacturing:
a. Siemens: Offers edge AI solutions for predictive maintenance, quality control, and automation in manufacturing. Their Siemens Industrial Edge platform provides edge devices with AI capabilities for analyzing sensor data, optimizing machine performance, and implementing predictive maintenance strategies.
b. Cognex: Provides machine vision systems and edge AI solutions for quality inspection and defect detection in manufacturing processes. Their In-Sight Edge devices enable on-device image analysis for real-time quality control and production optimization.
4. Transportation:
a. NVIDIA: Offers edge AI solutions for autonomous vehicles, traffic management, and fleet monitoring. Their NVIDIA Drive platform provides hardware and software solutions for autonomous driving, including AI processors and development kits for edge computing.
b. Mobileye (Intel): Provides edge AI solutions for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving. Their Mobileye EyeQ chips enable on-device processing of sensor data for real-time object detection, lane keeping, and collision avoidance.
5. Smart Cities:
a. Cisco: Offers edge AI solutions for smart city applications, including public safety, infrastructure monitoring, and energy management. Their Cisco Kinetic for Cities platform provides edge computing capabilities for analyzing data from IoT sensors and devices deployed in urban environments.
b. Bosch: Provides edge AI solutions for smart city infrastructure, including video analytics, traffic management, and environmental monitoring. Their Bosch Video Analytics solution uses edge devices to analyze video feeds for detecting security threats, traffic congestion, and air quality issues.
These companies, among others, are at the forefront of developing and deploying edge AI solutions to address various use cases in healthcare, retail, manufacturing, transportation, and smart cities.
Requirement for faster adoption of Edge AI
To facilitate faster adoption and implementation of edge AI solutions in products, several key services are essential. These services help address technical challenges, streamline development processes, and ensure successful deployment. Here are some critical services required:
Consulting and Advisory Services: Companies need guidance on understanding their specific requirements, identifying suitable edge AI use cases, and formulating an implementation strategy. Consulting firms specializing in edge AI can provide valuable insights, assess feasibility, and recommend the most effective approaches for integrating AI into products.
Custom Development and Integration: Tailored development services are necessary to design and implement edge AI solutions that meet the unique needs of each product. This includes developing custom machine learning models, optimizing algorithms for edge deployment, and integrating AI capabilities seamlessly into existing products or systems.
Edge Computing Infrastructure: Edge AI solutions require appropriate hardware and infrastructure to support computation and data processing at the edge. Service providers offering edge computing solutions can help companies select and deploy edge devices, edge servers, and edge computing platforms optimized for AI workloads.
Data Annotation and Labeling: High-quality labeled data is crucial for training and validating machine learning models used in edge AI applications. Data annotation services provide efficient labeling of training datasets, ensuring accuracy and consistency in model training and improving the performance of edge AI algorithms.
Model Training and Optimization: Service providers specializing in AI model development and optimization can assist companies in training, fine-tuning, and optimizing machine learning models for edge deployment. This includes techniques such as model compression, quantization, and pruning to reduce model size and computational requirements while maintaining accuracy.
Edge AI Software Development Kits (SDKs) and Tools: SDKs and development tools tailored for edge AI enable developers to build, test, and deploy AI applications more efficiently. Providers of SDKs and tools offer libraries, APIs, and frameworks for developing edge AI applications, simplifying the development process and accelerating time-to-market.
Deployment and Management Services: Companies require assistance in deploying edge AI solutions at scale and managing them effectively. Deployment services help with installation, configuration, and integration of edge AI systems into existing infrastructure, while management services offer ongoing monitoring, maintenance, and updates to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Training and Support: Training and support services are essential for enabling product teams to understand and effectively utilize edge AI technologies. This includes training sessions, workshops, documentation, and ongoing support to help developers and engineers overcome challenges and leverage edge AI capabilities effectively.
By leveraging these services, companies can overcome implementation barriers, accelerate product development cycles, and achieve faster adoption of edge AI solutions, enabling them to deliver innovative products with enhanced AI capabilities to market more rapidly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the rise of edge AI represents a profound shift in the AI landscape, offering unparalleled opportunities for innovation and advancement across industries. However, unlocking the full potential of edge AI necessitates overcoming several technical challenges. These challenges underscore the critical importance of specialized services tailored to facilitate the seamless integration and adoption of edge AI solutions in products and systems. From consulting and advisory to custom development and integration, edge computing infrastructure, data annotation and labeling, model training and optimization, SDKs and tools, deployment and management, to training and support, a comprehensive suite of services is required to navigate the complexities of edge AI implementation. By leveraging these services, companies can transcend barriers, accelerate innovation, and gain a competitive edge in delivering cutting-edge AI-powered products and services to market more rapidly. As the adoption of edge AI continues to proliferate, it promises to reshape industries, drive efficiency, and unlock new possibilities, ushering in a future where intelligence is not just centralized in the cloud but distributed at the edge of the network.
References
1. Karthika, R. A. (2024). "Progress and Innovations in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning." ResearchGate.
3. Ghiyasvand, M., & Keshtkar, I. (2024). "Minimizing the expense transmission time from the source node to demand nodes." Journal of Combinatorial Optimization, Springer.
4. URL: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10878-024-01113-1
5. Wang, L., Banerjee, S., Cao, Y., Mou, J., & Sun, B. (2024). "A new self-embedding digital watermarking encryption scheme." Nonlinear Dynamics, Springer.
6. URL: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11071-024-09521-y
7. Chen, X., Gao, Y., Wang, L., Cui, W., Huang, J., & Du, Y. (2024). "Large language model enhanced corpus of CO2 reduction electrocatalysts and synthesis procedures." Scientific Data, Nature.
8. URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41597-024-03180-9
9. Mishra, N. (2024). "Green Fintech Revolution: Assessing The Impact Of Sustainable Finance Platforms On Environmental And Social Outcomes." ResearchGate.
11. Li, A., Zhang, D., Yu, L., Kang, X., Tian, S., & Wu, W. (2024). "Residual cosine similar attention and bidirectional convolution in dual-branch network for skin lesion image classification." Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, Elsevier.
12. URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S095219762400544X
13. Cho, W., Lee, H., & Gu, J. (2024). "Optimization Techniques and Evaluation for Building an Integrated Lightweight Platform for AI and Data Collection Systems on Low-Power Edge Devices." Energies, MDPI.
14. URL: https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/17/7/1757
15. Bhalgaonkar, S., & Munot, M. (2024). "Model compression of deep neural network architectures for visual pattern recognition: Current status and future directions." Computers and Electrical Engineering, Elsevier.
16. URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0045790624001083
17. Gadzama, W. A., Gabi, D., Argungu, M. S., & Suru, H. U. (2024). "The use of machine learning and deep learning models in detecting depression on social media: A systematic literature review." Personalized Medicine in Psychiatry, Elsevier.
18. URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2468171724000115